Bookkeeping
What is FOB Origin? What is FOB Origin, Freight Prepaid?
The term, which was defined as part of the International Chamber of Commerce’s (ICC), is the most common agreement when shipping internationally. When shipping products Internationally, it’s important to understand the FOB Incoterms® and how it affects your business dealings. In this article we will break down how FOB Incoterms® work to give you an understanding of how to use it throughout the order and shipment process. Free on Board (FOB) is a term used to describe a key point in shipping where goods are transferred to the shipping vessel. The transaction moves forward once the goods are placed on board, and the international transport process begins. This is an international trade term used to determine when the ownership and liability of the goods shift from the seller to the buyer.
FOB transfers ownership, with transport cost and insurance responsibilities, at loading on the carrier at the seller’s location, with the buyer taking control. DAP, however, shifts ownership and responsibility at the buyer’s specified destination, while the seller pays all the costs and risks until unloading. Meanwhile, DAP places more responsibility on the seller for the transport costs, streamlining the delivery process to the buyer’s designated destination. The buyer takes responsibility for the shipping process as ownership and responsibility are transferred when the seller’s location is where the carrier is loaded with the goods. This involves planning the shipment, selecting the carrier, and deciding on the routing.
b. What are the Buyer’s Responsibilities?
The transportation department of a forward-thinking customer could choose FOB shipping point terms over FOB destination ones to maintain tighter control over the logistics process. When a product is sold “FOB shipping point,” or ‘fob origin,’ the buyer assumes responsibility for the goods as soon as they are loaded onto the carrier at the point of origin. The buyer pays the seller or supplier nothing more than the cost of transporting the product to the designated shipment point. FOB Origin dictates that the buyer assumes responsibility for the goods as soon as they are loaded onto the carrier at the point of origin. This impacts shipping costs, risks, and the logistics process, as the buyer must manage these aspects from the point of origin. To mitigate these risks, sellers should consider their ability to absorb potential losses and manage shipping costs before agreeing to FOB Destination terms.
- Over decades, these terms have evolved to address changing trade dynamics and technological advancements.
- For FOB Origin, the buyer assumes all risks related to damage, destruction, and loss during transit once the goods are loaded onto the chosen mode of transport at the origin point.
- The buyer then takes care of the import formalities and transportation to the final destination.
- Under CPT, or “carriage paid to,” the seller pays for delivery of goods to a carrier or nominated location and assumes risks until the carrier takes possession.
In contrast to the FOB shipping point, the seller may bear the risk of loss and responsibility for transportation expenses while the goods are in transit. If you agree to FOB shipping point terms, remember to factor in the costs of shipping and import taxes to your location when negotiating price. Alternatively, work with the seller to add additional coverage for shipping costs into your contract.
Who pays the freight on FOB shipments?
Understanding the responsibilities, effectively negotiating freight costs, and adhering to best practices can lead to successful and cost-efficient transactions. Understanding the shipping process is crucial in FOB agreements, as it highlights the stages and responsibilities involved in transferring goods from seller to buyer. Clear communication and efficient logistics management are essential to mitigate potential issues. These provisions outline the point when responsibility for risk of loss shifts to the buyer, who covers the freight charges, delivery location and time, and the payment terms for the shipments. The choice between FOB Origin and FOB destination depends on the specific needs fob who pays freight of both parties.
FOB origin
By clearly defining these responsibilities, FOB helps businesses plan their logistics strategies more effectively. Buyers can calculate the total costs of a FOB agreement by combining the FOB price from the seller and requesting a quotation from their freight forwarding company for the logistics. There is a reason FOB shipping is so popular amongst buyers and sellers; each party’s responsibilities give them the most control while the cargo is in their territory. The advantage for the buyer when purchasing under FOB Incoterms is they have the most control over the logistics and shipping costs, which allow them to choose their shipping methods. The seller loads the goods onto a shipping vessel in China and covers the shipping costs and insurance. Upon arrival, the goods go through customs clearance, which the seller also handles.
Both parties must clearly understand their responsibilities and maintain open communication throughout the shipping process to address any issues that may arise. The seller bears no responsibility for the goods during delivery and any damages, loss, or theft is handled by the buyer. Fuel charges, insurance, customs tax, and all other shipping fees are also under the buyer’s financial responsibility. Shipping under FOB terms, the buyer is responsible for all costs and risks once the goods are loaded onto the shipping vessel, but will not cover the cost of International seafreight. It is not free by any means, and failure to understand this term can lead to discrepancies when shipping products abroad and additional problems. If the responsible party does not accept liability, should damage or another event occur, that could result in the filing of a claim.
- The terms are used interchangeably to describe a shipping agreement and signify the same rules and conditions regarding the transfer of risk and costs in international transactions.
- There is a reason FOB shipping is so popular amongst buyers and sellers; each party’s responsibilities give them the most control while the cargo is in their territory.
- Likewise, the buyer won’t officially add the goods to its inventory until they arrive and are inspected.
- Key export documents include the Bill of Lading, the commercial invoice, and the packing list.
- Shipping via FOB Incoterms from China is simple, straightforward, and the ideal way to ensure your products leave China safely and arrive at your destination seamlessly.
FOB Origin and FOB Destination: The Nitty-Gritty
Only when the purchase arrives in perfect condition does the buyer accept it and consider the sale officially complete. When goods are labeled as FOB shipping point, the seller’s role in the transaction is complete when the purchased items are given to a shipping carrier and the shipment begins. Free on Board is the term used in shipping to specify which party is responsible for the shipped goods and where the responsibilities begin and end.
To understand each designation, we must first understand the difference between place of origin and place of destination and freight collect vs. freight prepaid. Whether you’re a small business shipping products or a large enterprise managing global logistics, understanding FOB helps you ship smarter. We also recommend that newer importers work with a China third-party logistics company company to assist them in the process.
CIF includes the cost of freight and insurance, while FOB gives the buyer more control over shipping but requires them to handle freight and insurance costs. A further advantage to the buyer from a FOB pricing arrangement is that it presents all of the costs up to the point at which the goods are loaded onto the vessel. However, the buyer needs to be ready for the additional costs, along with shipping and import duties. FOB is part of the broader Incoterms, which are international rules for the interpretation of trade terms.
FOB transfers ownership at the loading point onto the carrier at the seller’s location, with the buyer taking responsibility for shipping. In CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight), ownership transfers when the ship’s rail goods are loaded, but the seller covers main carriage costs and provides insurance until the destination port. With a CIF agreement, the seller has more responsibility, paying for the transport costs and insurance, influencing cost distribution and risk allocation. Ultimately, the choice of FOB shipping term depends on the specific needs and requirements of the business. It’s crucial to carefully review the sales contract and understand the terms and conditions of the FOB shipping agreement before making a decision. By doing so, businesses can ensure they select the most suitable shipping terms to manage their costs and risks effectively.
The term CIF full form in Export refers to Cost, Insurance, and Freight, an essential Incoterm used widely in global trade. CIF defines the responsibilities of buyers and sellers when shipping goods overseas. Published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC), CIF requires the seller to bear costs and arrange insurance and freight until the goods reach the buyer’s destination port. In an FOB Destination agreement, the seller retains ownership and responsibility for the goods until they reach the buyer’s specified location. This means the seller is on the hook for all shipping costs, insurance, and customs clearance until the goods are safely delivered to the buyer’s destination.
The prepaid freight agreement says that the seller is responsible for the freight charges until the order arrives at the buyer’s destination. Then, the seller sends an invoice to the buyer for reimbursement when the items are delivered. When items are sold “FOB destination,” the title to the commodities may not pass to the buyer until the items are delivered to the buyer’s loading dock, post office box, residence, or place of business. Until the items have arrived at the buyer’s location, the seller retains legal responsibility for them. Once the products have arrived at the buyer’s location, however, the buyer assumes full legal responsibility for them. FOB destination point refers to a product sold to a customer after it arrives at the buyer’s destination.
Some Incoterms can be used only for transport via sea, while others can be used for any mode of transportation. When goods are labeled with a destination port, the seller stays responsible for damages, lost items, and other costs and issues until the shipment is complete. When the destination is the origin port, it’s known as the FOB shipping point. This centuries-old shipping term has evolved into a critical concept of determining reliability and ownership transfer. The internationalization of markets and technological progress in logistics, distribution, and communication mean this affects almost every product consumers buy.
FOT applies to domestic land transport, while FOB is used for international shipping by sea or inland waterway. FOB indicates the exact point where the seller’s obligations end, and the buyer’s responsibilities begin. This helps both parties clearly understand when the goods are officially transferred, avoiding confusion during the transaction. Negotiable between the buyer and the seller, FOB terms offer flexibility to customize the agreement according to their needs. The parties can collaboratively determine various aspects, such as the precise point of transfer, the selection of the carrier, and specific responsibilities.
This delay in revenue recognition can impact the seller’s cash flow and financial reporting, as the income from the sale is not realized until the delivery is complete. Failing to check whether a shipment is labeled as FOB shipping point or FOB destination can leave you uninsured, out of pocket, and responsible for damaged or unsellable goods. While the seller does bear higher costs under FOB destination, they can factor shipping costs into pricing. While FOB shipping point does transfer risk to the buyer, it may affect a seller’s reputation and sales conversion rate. Shipping costs are reduced, but fewer buyers are willing to accept shipping point terms, especially on large or fragile orders.
Bookkeeping
Chart of Accounts: A Complete Guide for Nonprofits
This is the final part of our three part series on the functions of money. Our hope is that this series helps everyone to better understand money at a base level. Properly understanding what meant by Unit Of Account might not seem very interesting and to be honest, learning about fundamental economic things rarely is! However today we’re going to explore how the emergence of Bitcoin might one day ignite a paradigm shift in the way we as a species measure value across the world and into the future. StudySmarter is a globally recognized educational technology company, offering a holistic learning platform designed for students of all ages and educational levels. We offer an extensive library of learning materials, including interactive flashcards, comprehensive textbook solutions, and detailed explanations.
On the other hand, a Unit of Account serves as a standardised measure for the pricing of goods and services in an economy. This function brings an essential consensus on the value of objects, enabling a clear, objective comparison between diverse commodities and services. Money facilitates the process of measuring and comparing economic values. Every piece of currency issued by the government represents a specific value which is based on the confidence the users, i.e., the public, have in that government. Therefore, Money functions as the Unit of Account by being a universally accepted measure of economic value.
At the core of Bitcoin’s uniqueness is its capped maximum supply of 21 million coins. This sets it apart from traditional fiat currencies, which can be endlessly printed. The limited supply aims to eliminate inflationary pressures, providing a stable foundation for a reliable Unit of Account.
We follow a strict editorial policy, ensuring that our content is authored by highly qualified professionals and edited by subject matter experts. This guarantees that everything we publish is objective, accurate, and trustworthy. Bitcoin has only been around since 2009 so it obviously isn’t as well known and embedded in everyone’s culture compared to something like gold or the Euro.
- This is especially true in countries experiencing high inflation, where foreign currencies may be used alongside the national currency for transactions and accounting purposes.
- This ability to hold its ‘worth’ is what facilitates saving, investing and other temporal aspects of financial planning.
- This is similar to how we use kilometres per hour (km/h) as the unit of measurement to measure the speed of a car to be 5 km/h.
Standard Unit of Currency
This uniformity paves the way for the smooth functioning of other monetary functions such as the medium of exchange and store of value. In most countries, the unit of account is represented by the standard unit of currency, like the U.S. dollar or the euro. This standard unit is used to label and price everyday transactions, ensuring consistency in financial reporting and statements. A unit of account is used for both assets and liabilities in grouped or ungrouped transactions for financial reporting purposes.
A Function of Money
Unit of account is when a money is used to measure the value of goods and services, for example a coffee might be valued at $5 USD. Medium Of Exchange is when people are widely using the money to buy or sell goods and services, for example they may give someone a $5 note to buy the coffee. In business the unit of account is what the company or organisation uses to do its annual reports in. For example they might complete their profit and loss statement or submit their taxes denoted in a specific currency such as USD.
You’ll gain insights into its fundamental definition, significance, and practical application in various economies. Distinctly, the article unfolds the various roles of money, considering its use as a unit of account, and also delves into the delicate interplay between store of value and unit of account. Prepare to grasp the true worth of money and its multifaceted implications within the field of macroeconomics. Bitcoin’s immunity to inflation makes it a potential contender for a consistent Unit of Account. This predictability instills confidence in businesses and individuals, facilitating more reliable long-term financial planning.
This means every financial transaction, whether it is buying groceries or calculating GDP, is measured using this unit. Similarly, in units of account Japan, the yen is used; in the United Kingdom, it’s the pound sterling, and so forth. Delving into the subject of macroeconomics, you will come across the term ‘Unit of Account’. As intricate as this term might sound, it forms a key foundation in understanding wider economic theories and models.
Join over 22 million students in learning with our StudySmarter App
This article delves into the intricacies of the unit of account, exploring its role in the economy, its historical context, and its modern applications. A unit of account1 is a standard numerical monetary unit of measurement of the market value of goods, services, and other transactions. Also known as a “measure” or “standard” of relative worth and deferred payment, a unit of account is a necessary prerequisite for the formulation of commercial agreements that involve debt.
- All these measured things aren’t just done for the present either, they’re constantly compared to historic trends or values from decades, centuries or even millennia ago.
- By retaining its value, it gives confidence that you can exchange it for roughly the same amount of goods and services in the future.
- Similarly, in Japan, the yen is used; in the United Kingdom, it’s the pound sterling, and so forth.
- They were valued for their intrinsic worth and were widely accepted for transactions over long distances.
- Known for its stability and low inflation, the Swiss franc is often used as a benchmark in financial markets.
- The structure allows for detailed financial tracking and simplifies the preparation of reports for board members, donors, grantmakers, and government entities.
In the modern economy, the unit of account is used in various forms, from checking accounts to digital currencies. Checking accounts, for example, allow individuals and businesses to conduct transactions using the standard monetary unit of their currency. Digital currencies like Bitcoin also serve as units of account, although their acceptance and stability vary.
How does inflation affect the unit of account?
This saved amount, if held in a reliable currency, will hold its value and the individual can plan to utilise it in the future. So, the ‘Store of Value’ feature of money supports financial planning, allowing for future investments and expenditures. However, for money to successfully act as a medium of exchange, it must be a trustworthy unit of account. Viewed from this perspective, it is evident that the unit of account feature of money significantly drives its function as a medium of exchange. As a medium of exchange, money is universally accepted in return for goods and services. In this role, money eliminates the inefficiencies and complications of barter systems.
If you were to buy a book priced at £10 and a toy costing £20, you are able to compare the values and make an informed decision based on your budget and needs. This is made possible because there’s a standard metric – the pound – enabling accurate comparison. Without the unit of account feature, the economic landscape would be chaotic – imagine having to barter goods or services without a standard value measurement!
It allows for the standardization of values, making it easier to conduct and record transactions. Without a unit of account, comparing the value of different items or services would be challenging. For instance, in a barter economy, determining the exact value of one good in terms of another can be cumbersome.
What Does Unit Of Account Cost Mean?
Policymakers would need to explore alternative methods for managing economic growth. A thoughtful, well-organized COA helps you stay compliant, build donor trust, track your impact, and manage your mission more effectively. Whether you’re just getting started or optimizing for growth, investing the time into building the right COA structure will pay dividends for years to come. Liabilities represent what your organization owes to others, such as unpaid bills or credit card balances.
A unit of account is a standard numerical monetary unit of measurement of the market value of goods, services, and other transactions. It is one of the three functions of money, alongside being a medium of exchange and a store of value. In essence, it acts as a yardstick that measures the worth of goods and services against one another.
Bookkeeping
How to Start a Successful Solo Accounting Firm

As a small business owner, she is passionate about supporting other entrepreneurs and sharing information that will help them thrive. You should consider hiring a professional if your finances get too complicated or if you feel overwhelmed by bookkeeping tasks. Self-employed bookkeeping is keeping track of all your business money, like what you earn and what you spend. Keeping track of income helps in making informed decisions about the business’s future. Once registered, they’ll send you a unique tax reference, which you should keep hold of to submit your tax returns. Freelance accounting is different to working full-time in an accountancy firm or in-house department for a number of reasons.
- Transfer the numbers from your bank statements starting from the start date you chose in #4, filling out the details on your spreadsheet along with the categories.
- Compare features, pricing, and expert reviews for your business software needs – all in one place.
- Stability, investing in yourself, and running your business takes a combination of apps, knowledge, and grit.
- Having your books organized and matching your bank accounts is crucial to the success of your freelance finances.
- And pop the tax deadlines in your calendar, so you don’t miss them.
The UK’s Most Trusted Accountancy Firm
When tax time comes around, you can claim back certain business expenses, known as ‘allowable expenses’. These are deducted from your income before tax – so claiming the correct expenses ensures you’re paying the right amount of tax. We share Accounting Security a full list of allowable expenses here, but things like equipment expenses, software expenses, business mileage deductions, and office costs are typically included.
- However, regular face-to-face meetings are still valuable and can be much more productive in getting added value from your accountant.
- If you’re a sole trader and bookkeeping means nothing to you or you keep trying to put together spreadsheets but get stuck on what to include, then this guide will be helpful to you.
- Salaries vary widely depending on experience, specialism, and even your location.
- You can also improve your accounting project management skills with the help of workflow experts like Kellie Parks, CPB, Ron Baker, and Heather Satterley, CPA from Accounting Workflow Academy.
- Neither Atomic Invest nor Atomic Brokerage, nor any of their affiliates is a bank.
- If this detailed quote is logged in your accounting system, it serves as a contract once the customers agree on the terms.
Choose the right software
In the real world, it takes patience to reach the point where business is booming and everyone knows your name. “It took about seven or eight years to grow the business and turn it around,” Lessin says. When you’re on your own and having to get the work done, it’s hard to find time to do the marketing and networking that will help grow your business. Of course, you could hire someone else to do that—if you’re bringing in enough money, that is. Before you leave your day job to go it alone it’s important to have a proper plan. This is a great option if you’re still studying, want a taste of running your own business or want to specialise in bookkeeping.

Why choose our self employed accounting services?
It’s best to enter income into your bookkeeping system as soon as payment is received. This could be done daily, weekly, or monthly, depending on how often transactions occur. These features can significantly enhance the efficiency of managing finances. Becoming self-employed also now means that you self employed accountant could be liable for any mistakes you make in relation to your accounting services. Insurance for accountants is designed to protect you from risks that could occur as a result of your profession.

Logging Income Regularly

Most firm owners forget to tap into their existing relationships when networking. Checking on your existing relationships to see how their businesses are doing can remind them of your services, which may result in repeat business. You can’t run a successful solo accounting firm without knowing who your ideal client is and what keeps them up at night. The more of your ideal client you know, the easier it will be for you to complete projects and earn well. We provide Accounting Periods and Methods different levels of support, depending on the plan and/or the add-on features you choose. You work hard to make your business a success—that’s why Wave uses both physical and digital protection to keep your money safe.
Bookkeeping
Issue of Shares Journal Entries: At Par, Premium and Discount
It’s essential to keep track of these changes to accurately represent a company’s equity. The book value of a corporation is equal to its total stockholders’ equity, which is $78,000 in our example. A corporation must declare a dividend before it can distribute cash to its stockholders, and the declaration date is when the liability for the dividend is created. Common shares are a crucial part of a corporation’s ownership structure, and understanding them is essential for any investor or business owner. The company spends $ 5.5 million to purchase the shares and keep them on the balance sheet.
- Common stock is a financial instrument that represents the ownership of a company.
- This is similar to “shares authorized,” the maximum number of shares a company is allowed to issue.
- Some companies may also have other options when raising finance from this source.
- In exchange for these instruments, the company issues shares, which provide the holder with several rights.
In other words, the company needs to post lucid journal entries so that the correct amount appears under each head. The company can make the journal entry for the issuance of common stock for cash at par value by debiting the cash account and crediting the common stock account. When recording the issuance of common stock, companies must consider whether the stock has a par value or is no-par value. Par value is a nominal amount assigned to each share, often set at a minimal figure, serving as a legal capital threshold. No-par value stock does not have this nominal amount, allowing for greater flexibility in pricing shares.
So, the fair value of the shares of the common stock given up will be used as the measurement if its market value is available. However, if the fair value of the shares of the common stock giving up cannot be determined, the fair value of the service expense will be used instead. As mentioned, we may issue the common stock in exchange for the non-cash asset, such as land, building or equipment, etc. instead of the cash asset. In a corporation, the common stock is usually issued for a higher value than its par value. Stock split is the process of dividing the current share number into multiple new shares to boost the stock liquidity.
Issuance of Shares of Stock
To calculate the book value per share of common stock, you divide the total stockholders’ equity by the number of shares outstanding. In our example, this is $78,000 divided by 2,000 shares, which equals $39 per share. The record date merely determines the names of the stockholders that will receive the dividends, and dividends are paid only on outstanding shares of stock. In some cases, the number of shares outstanding can change throughout the year, which affects the earnings per share calculation.
Journal Entries for Stock Splits and Dividends
- Accountants generally record the transaction at the fair value of (1) the property or services received or (2) the stock issued, whichever is more clearly evident.
- Book value can be calculated in various ways, including the book value of an asset, bonds payable, a corporation, common stock, and preferred stock.
- The deficit of $2 per share ($8 minus $10) is called a discount on common stock.
- Outstanding shares are a key concept in understanding a company’s equity.
A stock split adjusts the number of shares outstanding without affecting the total value of equity. Forward splits increase the number of shares and reduce the share price, making them more accessible to a broader range of investors. Conversely, reverse splits decrease the number of shares and increase the price, often used to meet stock exchange listing requirements.
Issue Common Stock for Non-Cash
This includes the issuance at par value, at no par value, at a stated value, and the issuance for non-cash assets. In exchange for these instruments, the company issues shares, which provide the holder with several rights. The latter source of finance comes from third parties, such as banks and other financial institutions. When it issues no-par stock with a stated value, a company carries the shares in the capital stock account at the stated value.
3 Accounting for the issuance of common stock
The book value per share of common stock is calculated by dividing the total stockholders’ equity by the number of shares outstanding. For instance, if a corporation has $78,000 in stockholders’ equity and 2,000 shares of common stock outstanding, the book value per share is $39. Hence, we may come across the circumstance in which the common stock has no par value (e.i., no par value registered on the stock certificate).
3.3 Common stock issuance costs
The second feature that differentiates common stock from others is voting rights. These voting rights allow the shareholders to dictate how the company operates. For example, they can elect the board of directors and vote on a company’s policies. However, the same rights are not a part of the other types of stock that companies offer, for instance, preferred stock. Bonus issue is not cash transaction That just shifts reserves to share capital. This is under the problems of issue of bonus shares journal entries pdf.
Issue of shares at par is when a company issues shares at the same value as the face value. To explain, if a share’s face value is ₹10 and the company offers the share at a price of ₹10, it would be par value. It is a key detail for companies accounts issue of shares journal entries, and readers will need clarity on how each case affects the accounts. Issue of shares refers to offering a company shares to the public or to private investors Companies do this to fund operations, to expand or to pay off loans.
Through this, the whole sum is credited to the Share Capital Account. PwC refers to the US member firm or one of its subsidiaries or affiliates, and may sometimes refer to the PwC network. This content is for general information purposes only, and should not be used as a substitute for consultation with professional advisors.
DeWitt carries the $ 30,000 received over and above the stated value of $200,000 permanently as paid-in capital because it is a part of the capital originally contributed by the stockholders. Book value is used to calculate the value of a corporation’s assets, bonds payable, and stockholders’ equity. The book value of a corporation is equal to the total amount of stockholders’ equity. To pay a dividend, the company must have sufficient cash and a positive balance in retained earnings, and there is no mandatory dividend requirement. Accurate accounting for equity issuance is crucial for several reasons, including financial transparency, regulatory compliance, and internal decision-making.
A corporation with 2,000 shares of stock outstanding has already issued those shares to investors. The common stock, sometimes, is issued for non-cash assets; for example in exchange for land or building, or sometimes in exchange for not paying organization expenses to the promoters. Such non-cash assets are then recorded at the market values as of the date of transactions.
Par value shares are those which have a face value assigned to them. Kellie Hessel is a rising star in the world of journalism, with a passion for uncovering the stories that shape our world. Equity issuance can be executed through public offerings or private placements. This process enables companies to obtain funds for various purposes, such as expanding operations or paying off debt. A company has no obligation to pay a dividend, and there is no “liability” for dividends until such time as they are actually declared.
It represents the maximum share that the company able to issue in the future. However, it does not mean that company needs to issue all the authorized shares. Alternatively, if the company ABC issues the stock at a price that is higher than the par value, the difference will be recorded as additional paid-in capital. APIC serves as a financial buffer, providing companies with a reserve that can be leveraged for future growth initiatives or to weather financial downturns.
Funds accumulated issuing common stock journal entry in APIC can be utilized for research and development, acquisitions, or other strategic investments that drive long-term value creation. APIC can enhance a company’s balance sheet, making it more attractive to potential investors by showcasing a robust equity position. A stock split will not change the general ledger account balances, so the dollar amounts reported in the stockholders’ equity section of the balance sheet will not change. To calculate earnings available for common stockholders, we need to know the corporation’s net income after income tax, which is $10,000.
For some companies, the terms may differ, for example, paid-in capital and additional paid-in capital. In essence, however, the accounting treatment for the issuance of common stock will remain the same. Since the company may issue shares at different times and at differing amounts, its credits to the capital stock account are not uniform amounts per share. This contrasts with issuing par value shares or shares with a stated value. In some states, the entire amount received for shares without par or stated value is the amount of legal capital.
The common stock can be issued with par value and without par value. Facebook’s IPO was a significant event in the company’s history, raising $16 billion by issuing 421.2 million shares at $38 per share. This massive influx of cash enabled Facebook to expand its business operations and make strategic acquisitions. Outstanding shares can change over time due to reacquisitions or new issuances.
-
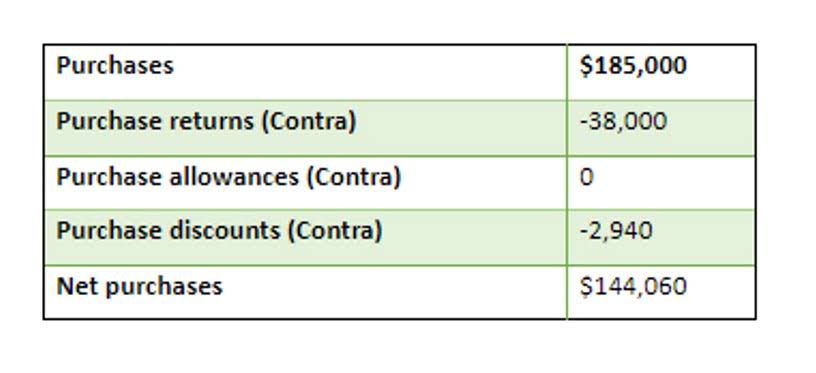
 Venture Capitalist Firms5 years ago
Venture Capitalist Firms5 years agoA Failing Grade
-
 Venture Capitalist Firms5 years ago
Venture Capitalist Firms5 years agoSome Email Stats
-
 Venture Capitalist Firms4 years ago
Venture Capitalist Firms4 years agoMost Read Blog Posts
-

 Investors5 years ago
Investors5 years agoShifting corporate responsibility to consumer resilience
-
 Investment5 years ago
Investment5 years agoChinese Government Bonds: The Elephant in the Room
-

 Investors5 years ago
Investors5 years agoLast Days of The True Tiger Blog!!
-

 Venture Capitalist Firms2 years ago
Venture Capitalist Firms2 years agoDear SaaStr: What Percentage of Software Sales Reps Have Earned Over $1m a Year?
-
Venture Capitalist Firms5 years ago
Investing In Learning

